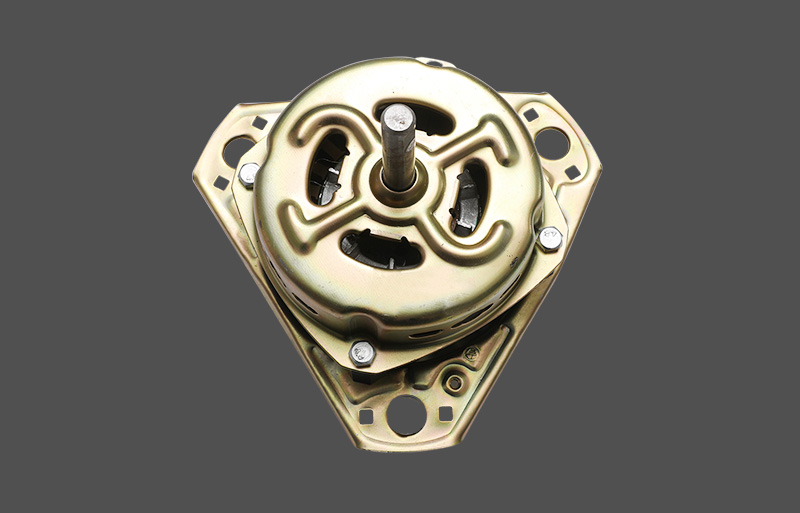
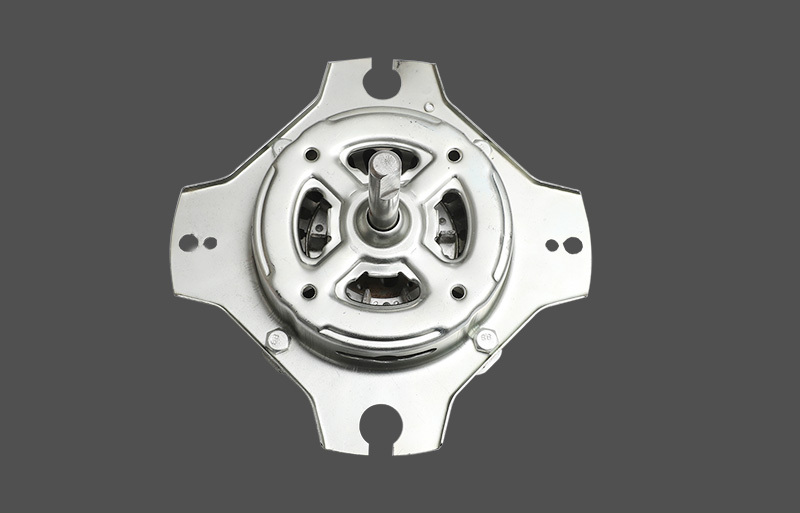
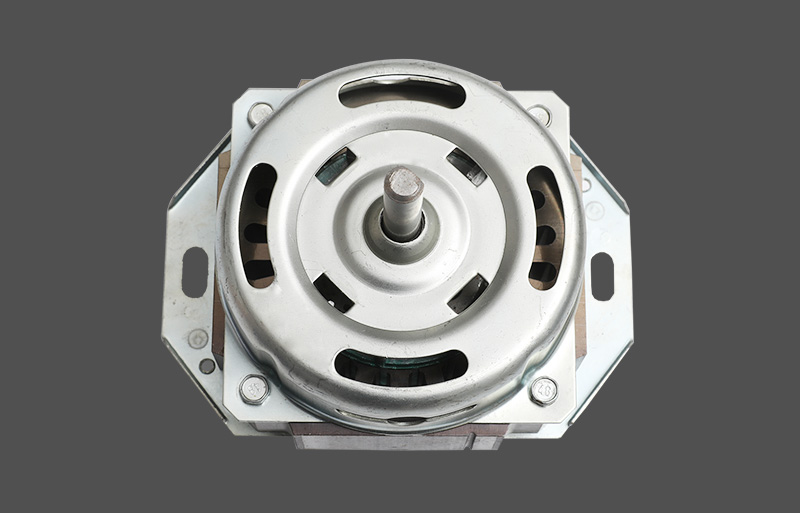
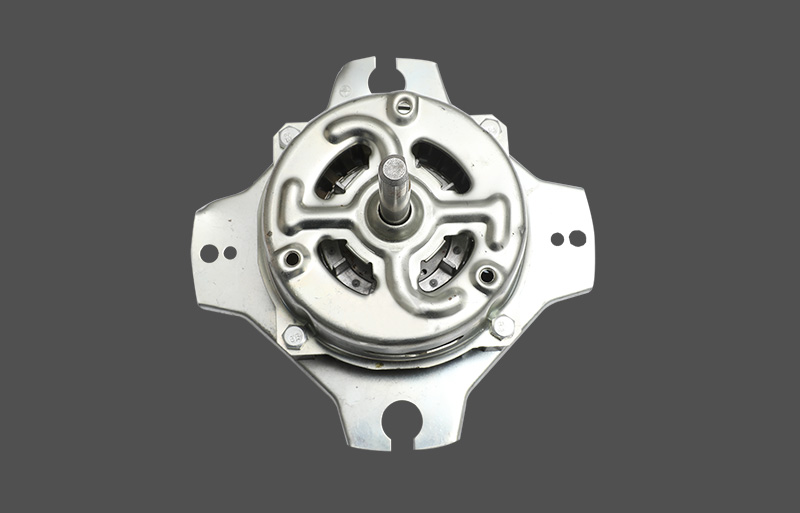
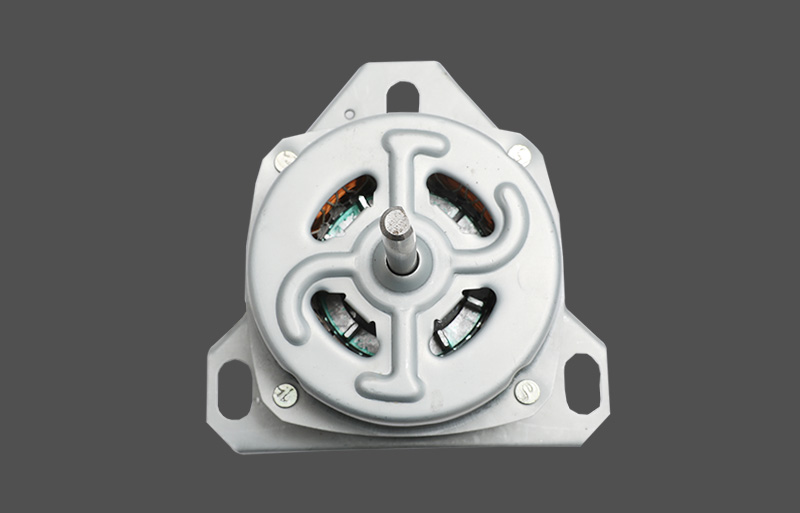
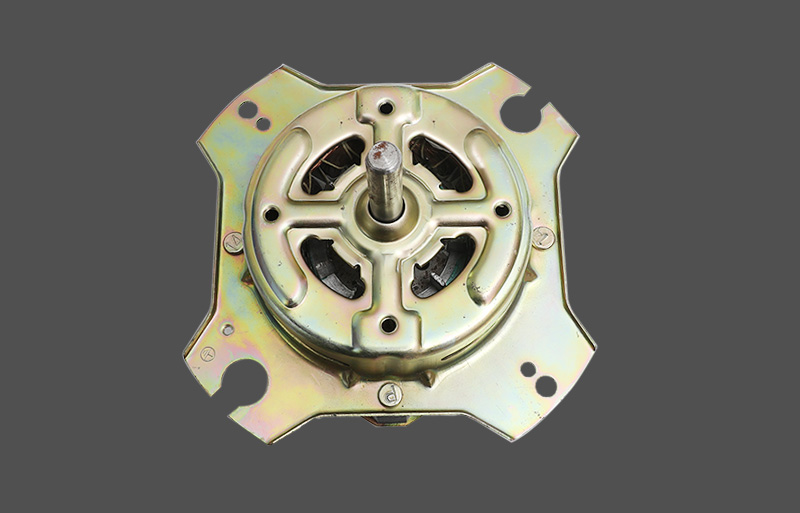
Den stående ventilatormotor er kernekomponenten for både husholdnings- og kommercielle fans. Under drift kan den opleve overophedning, hvilket kan påvirke motorens levetid og driftssikkerhed. En veldesignet termisk beskyttelsesmekanisme er afgørende for stabil ydeevne og holdbarhed. Denne artikel giver et professionelt overblik over designprincipper, typer, mekanismer og anvendelser af termisk beskyttelse i stående ventilatormotorer.
Betydningen af termisk beskyttelse
Motorviklinger kan overskride sikre temperaturgrænser under langvarig drift eller høje belastningsforhold, hvilket fører til ældning af isoleringen, lejeskader og endda motorudbrænding. Overophedning kan også udgøre brandfare eller elektriske sikkerhedsrisici. Termiske beskyttelsesmekanismer overvåger motortemperaturen i realtid og aktiverer beskyttelsesforanstaltninger, når det er nødvendigt, hvilket sikrer pålidelig drift. I stående ventilatorer beskytter termisk beskyttelse ikke kun motoren, men forbedrer også produktkvaliteten og brugeroplevelsen.
Typer af termiske beskyttelsesmekanismer
Denrmal protection in standing fan motors is generally categorized into mechanical and electronic types. Mechanical protection often uses bimetallic strips or thermal switches, which disconnect the circuit based on thermal expansion properties. Electronic protection employs temperature sensors or thermistors (NTC/PTC) to measure temperature, with control circuits determining whether to cut power or reduce load. Electronic protection offers faster response and higher accuracy, enabling multi-level temperature control and fault alarm functions. Mechanical protection is cost-effective and simple, commonly applied in low-power household fans.
Udløsende princip for termisk beskyttelse
Denrmal protection activation is based on temperature detection and threshold judgment. Mechanical switches use thermal expansion to open contacts and disconnect power. Electronic protection converts temperature readings into voltage or resistance signals, allowing control chips to determine whether the motor exceeds preset temperature thresholds. When excessive heat is detected, the system can immediately cut power, reduce speed, or implement intermittent operation. Designers must consider sensor placement, response time, and hysteresis to avoid false triggers and ensure reliable protection.
Nøgledesignparametre
Nøgleparametre i termisk beskyttelsesdesign omfatter temperaturtærskler, responstid, nulstillingsmetoder og installationssted. Tærskelværdier bestemmes baseret på motorens nominelle effekt, isoleringsklasse og driftsmiljø, typisk omkring 120 ℃ for husholdningsblæsermotorer. Responstid påvirker direkte beskyttelseseffektiviteten; hurtigere respons forhindrer motorskader. Nulstillingsmetoder omfatter automatisk og manuel nulstilling. Automatisk nulstilling passer til kontinuerlig drift, mens manuel nulstilling øger sikkerheden i højrisikoapplikationer. Sensorer bør placeres i nærheden af snoede eller hotspot-områder for nøjagtigt at afspejle kritiske temperaturer.
Koordinering med varmeafledning
Denrmal protection works best when combined with effective heat dissipation. Proper airflow design, installation of heat sinks, and blade arrangement reduce localized motor temperatures, improving protection accuracy. Good heat dissipation delays temperature rise, reducing frequent protective trips and extending motor lifespan. Thermal simulation can evaluate temperature distribution, ensuring the protection device functions at key hotspots.
Overvejelser om pålidelighed og lang levetid
Denrmal protection devices in standing fan motors must exhibit high reliability and long operational life. Mechanical switches should withstand multiple thermal cycles without failure, while electronic sensors require high precision and resistance to electrical interference. Selecting high-quality materials, optimizing contact structures, and implementing moisture and dust protection enhance reliability. A robust thermal protection system prevents motor burnout and accidents during long-term use, ensuring product safety.